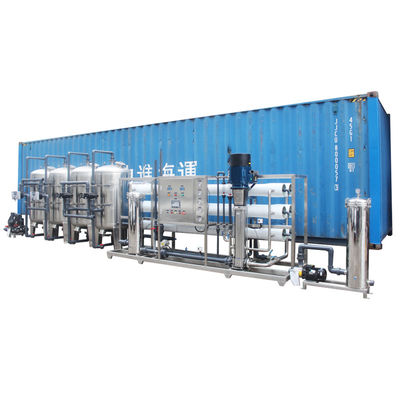
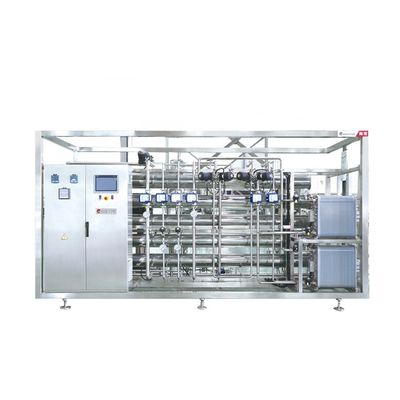
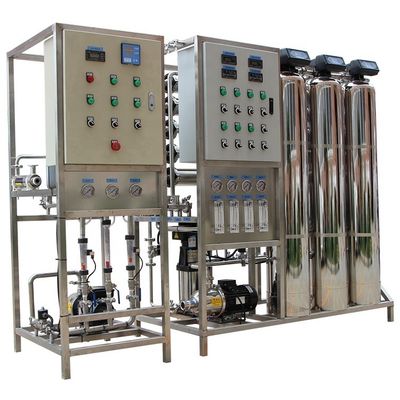
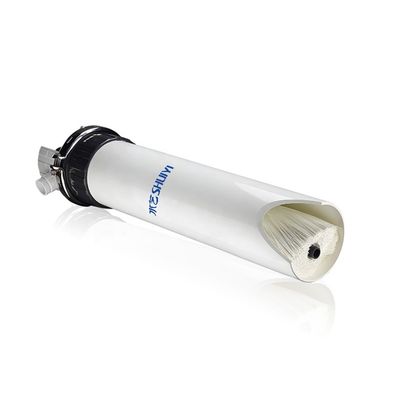
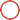
Reverse osmosis is a membrane separation technique that uses pressure
as a driving force by selecting a function of permeating (semi-transmissive) membrane.
When the pressure applied in the system is greater than the osmotic pressure of the aqueous solution,
the water molecules continuously permeate the membrane.
The impurities flowing into the central tube through the product water channel
and then flowing out of the water at one end, such as ions, organic matter, bacteria, viruses, etc.,
are trapped on the water inlet side of the membrane, and then flow out at the concentrated water outlet end,
thereby achieving the purpose ofseparation and purification.